When it comes to purchasing a home, understanding your mortgage options is crucial. Mortgages play a vital role in the home buying process, allowing individuals to finance their dream homes while managing their financial obligations effectively. However, navigating the world of mortgages can be overwhelming, especially for first-time homebuyers. This comprehensive guide will answer some of the most frequently asked questions about mortgages, such as what mortgage you can get, how much mortgage you could get, what mortgage you can qualify for, how much mortgage you can afford, and how much mortgage you afford. So, let’s dive in!

What Mortgage Can I Get?
Securing the right mortgage for your needs is essential. To determine what mortgage you can get, several factors come into play. Lenders evaluate your credit score, income, debt-to-income ratio, employment history, and down payment. These factors help lenders assess your financial stability and determine the type of mortgage and loan amount you qualify for.
- In addition to your financial information, lenders will also consider the current interest rates and the term length you desire. Different mortgage products, such as fixed-rate mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages, offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. It’s crucial to understand the details of each mortgage option to make an informed decision.
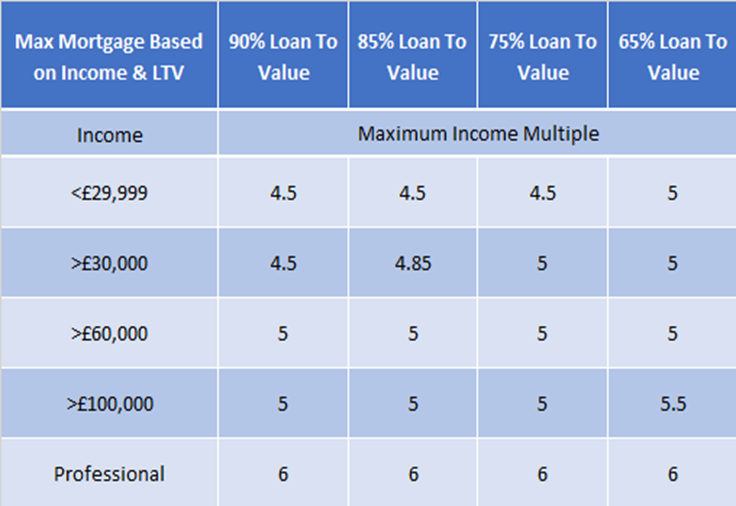
How Much Mortgage Could I Get?
- Determining how much mortgage you could get involves assessing your financial situation and the affordability of your monthly payments. Lenders typically follow a guideline called the debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, which measures your monthly debt payments against your gross monthly income.
- To calculate your DTI ratio, add up all your monthly debt payments, including credit card bills, car loans, student loans, and any other outstanding debts. Then divide that total by your gross monthly income and multiply by 100 to get a percentage. Lenders generally prefer a DTI ratio below 43%, although specific requirements may vary.
- Another aspect to consider when calculating how much mortgage you could get is your down payment. A higher down payment reduces the loan amount needed and can increase your chances of securing a larger mortgage. However, it’s important to strike a balance between your down payment and maintaining a comfortable level of savings for unexpected expenses or emergencies.
How Much Mortgage Could I Get?
- Qualifying for a mortgage depends on various factors, including your credit score, income, and employment history. Lenders use this information to assess your creditworthiness and determine the level of risk associated with lending to you.
- Your credit score is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness, ranging from 300 to 850. A higher credit score indicates lower risk, making it easier to qualify for a mortgage with favorable terms. Lenders also consider the length of your credit history, the number of open credit accounts, and your payment history.
- In addition to your credit score, lenders evaluate your income stability and employment history. They want to ensure that you have a consistent and reliable source of income to make timely mortgage payments. Providing proof of stable employment and income, such as pay stubs and tax returns, can increase your chances of qualifying for a mortgage.

How Much Mortgage Can I Afford?
- Understanding how much mortgage you can afford is crucial to avoid stretching your finances too thin. By carefully evaluating your income, expenses, and financial goals, you can determine a mortgage payment that fits comfortably within your budget.
- To assess how much mortgage you can afford, consider your monthly income and debt obligations. Lenders typically follow the 28/36 rule, which suggests that no more than 28% of your gross monthly income should go towards housing expenses, and your total debt payments should not exceed 36% of your income.
- To calculate how much mortgage you can afford, consider your monthly income, expenses, and savings goals. As a general rule, financial experts recommend allocating no more than 28% of your gross monthly income towards housing costs, including mortgage payments, property taxes, and home-owners insurance.
- It’s also important to account for other monthly expenses, such as utilities, groceries, transportation, and debt repayments. By creating a comprehensive budget and considering your overall financial picture, you can determine a mortgage payment that aligns with your financial goals and provides a comfortable living situation.
- However, it’s important to remember that these are general guidelines, and everyone’s financial situation is unique. Factors such as your overall debt load, future financial goals, and personal preferences should also be taken into account when determining how much mortgage you can afford.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
FAQ 1: Can I get a mortgage with bad credit?
Yes, it’s possible to get a mortgage with bad credit, but it may be more challenging. Lenders may require a higher down payment, charge a higher interest rate, or offer a mortgage with less favorable terms. Working on improving your credit score and demonstrating financial stability can increase your chances of securing a mortgage with better terms.
FAQ 2: Can I qualify for a mortgage with self-employment income?
- Yes, self-employed individuals can qualify for a mortgage. However, the process may require additional documentation to verify your income and stability. Lenders may request tax returns, profit and loss statements, and other financial documents to assess your eligibility for a mortgage.
FAQ 3: What is the difference between prequalification and preapproval?
- Prequalification is an initial assessment of your financial situation based on self-reported information. It provides an estimate of how much you may be able to borrow but is not a guarantee of a loan. Preapproval, on the other hand, involves a thorough review of your financial documents and credit history. It provides a more accurate assessment and a conditional commitment from the lender.
FAQ 4: How does a larger down payment affect my mortgage?
- A larger down payment reduces the loan amount you need to borrow, which can result in lower monthly payments and interest charges. It can also improve your chances of qualifying for a mortgage and help you avoid private mortgage insurance (PMI) if you can make a down payment of 20% or more.
FAQ 5: Can I pay off my mortgage early?
- Yes, it’s possible to pay off your mortgage early by making extra principal payments. By reducing the principal balance, you can save on interest charges and potentially pay off your mortgage ahead of schedule. However, it’s important to review your mortgage agreement for any prepayment penalties or restrictions.
FAQ 6: How does refinancing a mortgage work?
- Refinancing a mortgage involves replacing your existing mortgage with a new loan. The new loan may have different terms, interest rates, and monthly payments. People often refinance to take advantage of lower interest rates, shorten the loan term, or access equity in their home.
FAQ 7: What is mortgage prepayment penalty?
- A mortgage prepayment penalty is a fee charged by some lenders if you pay off your mortgage before a specified period, typically within the first few years of the loan. This penalty is designed to compensate the lender for potential lost interest income.
FAQ 8: Can I get a mortgage with a low-down payment?
- Yes, there are mortgage options available for buyers with a low-down payment. Government-backed loans such as FHA loans and VA loans often offer lower down payment requirements, allowing buyers to finance a home with as little as 3.5% down for FHA loans and zero down for eligible veterans with VA loans.
FAQ 9: What is mortgage insurance?
- Mortgage insurance is a type of insurance that protects the lender in case the borrower defaults on the loan. If you make a down payment of less than 20% on a conventional mortgage, lenders usually require private mortgage insurance (PMI). FHA loans and some other government-backed loans have their own mortgage insurance requirements.
FAQ 10: What is an escrow account?
- An escrow account is an account held by the lender to pay for property taxes and insurance on behalf of the borrower. A portion of the monthly mortgage payment is deposited into the escrow account, and the lender uses those funds to pay for these expenses when they are due. This helps ensure that property taxes and insurance premiums are paid in a timely manner.
FAQ 11: What is a mortgage rate lock?
- A mortgage rate lock is an agreement between the borrower and the lender to secure a specific interest rate for a set period of time, typically during the mortgage application process. This allows borrowers to protect themselves from potential interest rate increases while their loan is being processed.
FAQ 12: Can I refinance my mortgage if I have bad credit?
- Refinancing a mortgage with bad credit may be more challenging, but it’s not impossible. Lenders will consider factors such as your credit score, income, and loan-to-value ratio. You may have more options if you have improved your credit since taking out the original mortgage or if you have built equity in your home.
FAQ 13: What is a mortgage points?
- Mortgage points, also known as discount points, are fees paid to the lender at closing in exchange for a lower interest rate. Each point typically costs 1% of the loan amount and can reduce the interest rate by a certain percentage. Paying points upfront can lower your monthly mortgage payments over the life of the loan.
FAQ 14: What is an amortization schedule?
- An amortization schedule is a table that shows the breakdown of each mortgage payment over time. It includes details such as the principal and interest portions of the payment, the remaining loan balance, and the total interest paid. This schedule helps borrowers understand how their payments contribute to reducing the loan balance and building equity.
FAQ 15: Can I transfer my mortgage to another property?
- In most cases, you cannot transfer your mortgage from one property to another. When you sell your current home, the mortgage is typically paid off, and you would need to apply for a new mortgage for the new property. However, some lenders may offer options such as mortgage portability, allowing you to transfer your existing mortgage to a new property with certain conditions and requirements.
Remember, each individual’s mortgage needs may vary, and it’s important to consult with a qualified mortgage professional to get personalized advice based on your specific circumstances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of mortgages is essential when embarking on the journey of homeownership. By exploring the questions of what mortgage, you can get, how much mortgage you could get, what mortgage you can qualify for, how much mortgage you can afford, and how much mortgage you afford, you gain valuable insights into the mortgage process.
Determining, what mortgage you can get involves a careful evaluation of your financial situation, credit score, income, and down payment. By understanding your financial standing, you can navigate the mortgage market with confidence and find the right loan option for your needs.
Leave a Reply